[Youtube学习笔记]Linux的50个实用指令
-
50 Most Popular Linux and Terminal Commands
这篇文章的内容主要来源于Youtube视频The 50 Most Popular Linux & Terminal Commands - Full Course for Beginners
建议大家可以follow一下这个博主来支持。另外,推荐这个网站 Linux Commands Handbook,里面有可以查询的Linux指令。
为什么要掌握这些指令呢?
- 更好地控制你的电脑
- 运行速度很快
- 可以自动化很多工作
操作系统
Linux和Mac都来源于一个叫做Unix的操作系统,因此可以指令基本是通用的。但是Windows有一套自己的系统。
Linux本身是指一个Kernel, Kernel就是链接application和CPU / Memory的东西。在Windows上安装LInux
windows一般是不可以直接用Linux指令的,但是现在我们可以用下面的命令来在Windows里面安装一个小的Linux系统。
wsl --install电脑上用管理员权限运行 PowerShell (不是 PowerShell(86) )
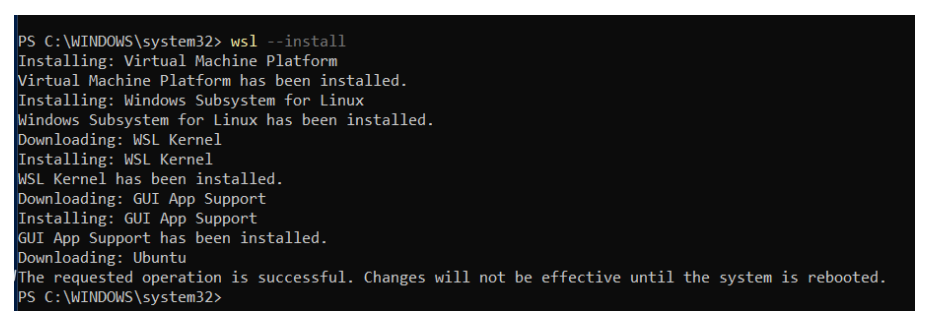
重启电脑后就可以搜索到一个叫做Ubuntu的程序

打开这个程序后,需要自定义用户名和密码(用户名需要是小写英文)
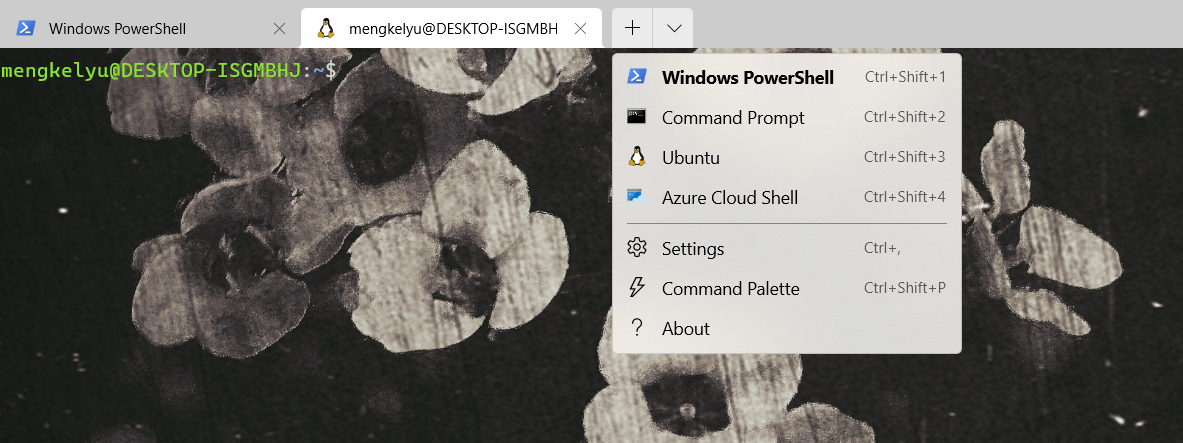
然后就可以在这里运行Linux指令啦为了更好地运行这些不同的Shell,可以安装一下Windows Terminal。(免费软件,在Microsoft Store里面可以安装)
安装后,它可以允许我们自定义运行命令的背景等等。如果我们要运行一个Windows Powershell,可以点击加号,有不同的Shell可供选择
Basics
一些基本指令
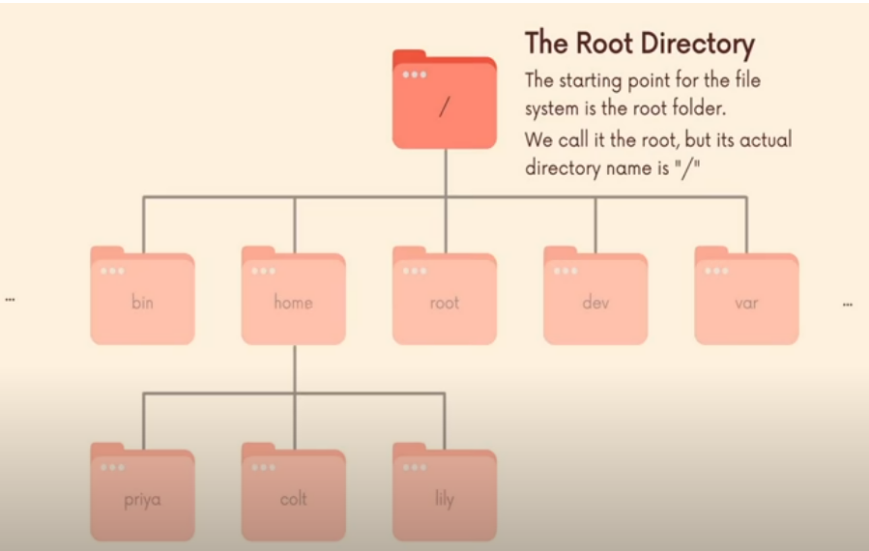
whoami 'print the username man <command> 'open a manual for that command man whoami clear 'clear the terminal screen clear -x 'clear the terminal screen but remains the history pwd 'print working directory ls 'list a contents of the current folder ls <target folder path> 'list the contents for a target folder ls -l 'long format of files. (with file names etc) ls -a 'does not hide files starting with . cd 'change directory cd .. 'Go back to previous folder cd ~ 'Go to the folder with username help <command> 'the help file for any commandLinux File Structure.
All absolute path starts with /
In the home folder, for all users using this machine, there will be a username for him/her
mkdir #make a directory 创建一个文件夹 mkdir a b #make two folders 创建 a 和 b 两个文件夹 mkdir -p a/b #create parent directory when necessary 在文件夹 a下创建文件夹 b, 如果文件夹a不存在,先创建文件夹a,再创建子文件夹b touch #change file timestamps. if a file does not exist, it creates this file for us 改变文件的时间戳,如果文件不存在,创建这个文件 (这个命令常常用于创建文件) rmdir #remove a directory (only for empty ) 删除空文件夹 rm #remove a file 删掉一个文件 rm -rv <folder> #recursively delete all files in a folder 删除文件夹中的所有文件 rm -V #print the output V参数可以输出删掉的内容 open #open a file or folder (mac only) mac中打开文件或文件夹的指令 open . #open the current directory 打开当前文件夹 xdg-open #open command in linux 打开文件在Linux中的指令,会用默认软件打开 mv #move files 移动文件 cp #copy a file or folder 复制文件或文件夹 cp -r #copy recursively for files in a folder 复制文件夹以及其中的所有文件 head #output the first part of files 输出文件的前部分 head <filename> -n <number> #n is for the number of lines to output tail #output the last part of files 输出文件的后部分 date #prints out the current date 输出当前日期 date > today.txt #output the current date to today.txt 输出当前日期到文件today.txt date >> today.txt #appending to a file instead of rewrite it 输出当前日期,并把当前日期写在today.txt文件后面,而不会删除原本内容
-
cat file #print all contents of a file 输出一个文件中的全部内容 cat file1 file2 #print all contents of file1 and file2 输出文件1和文件2的全部内容 cat -n file1 #-n is to print out the line numbers 加入参数n,可以同时输出内容和行数 less <file># it shows the content stored inside a file, in a nice and interactive UI; cat的漂亮形式 echo #it prints to the output the argument passed to it 这个命令等于print wc #print number of lines; number of words; number of bits 输出基本信息,(多少行,多少数字,多少bit) | #give the output of the first argument to the second argument 这个符号可以把符号前面的Output传递给符号后面的命令作为Input ls -l | wc #word count for the ls -l 比如这个例子,ls -l 输出了当前文件夹下所有文件的名字,然后这个文本传递给了wc输出文本的基本信息 sort #sort the document 给文件排序 sort -n file #sort everything numerically 按照数字顺序给文件排序 uniq #report or omit repeated lines uniq -d #only report duplicated values uniq -u #only report non-duplicated values uniq -C #count how many times each value is duplicated *.txt #match all documents ending with txt ? #match one character {a,b,c}.txt #output a.txt, b.txt, c.txt Day{1..365} #output Day1 Day2 Day3 .... Day 365 diff #compare the contents of two files diff -v file1 file2 #compare two files line by line find <directory> <critria> find . -name #*.txt# find . -iname #*.Txt# #i for case incensitive find . -type d #only search for directory find . -type f #only search for files find . -name #E*# -or -name #*E# find . -type f exec cat {} \ #exec cat to every file. {} is placeholder for each found result grep #help search inside files grep <string to be found> <text to search> grep -r <string to be found> <directory> #recursively found a string in all texts in a folder. -ri can make it case incensitive du #find the size of directories or files df #show how many space left history #history of all commands run. Combined with grep, it is possible to obtain the command with certain character ps #view the process running on the computer top #display top 10 process kill #shut a process kill <PID> kill -9 #brutal kill kill -15 #gental kill killall #perform multiple kills jobs #print out commands fg <job number> #run some command on the foreground bg <job number> #run some command on the background <command> & #run the command on the backgound jobs #see those commands gzip <file name>#compress a file gzip -k <file name> #compress a file while keeping the original file gzip -d <file name>#decompress a file gunzip <file name>#decompress a file tar #used to create an archive, grouping multiple files in a single file tar -cf archive.tar file1 file2 #the c option standas for create, the f option is used to write to file the archive tar -xf #extract to current folder tar -czf archive.tar.gz file1 file2 #creating a tar achive and then running gzip on it nano #a friendly editor alias <new command name> = '<old command>'# Give some alias to a long command # difference of "" and '', "" allows variable in a string echo "home directory \$PWD" # 这里\$PWD被当作成了变量或参数 echo 'home directory \$PWD' # 这里\$PWD没有被当作成变量或参数 xargs # turn the output of first argument to the input of second arguement' find x -size +1M | xargs ls -lh ln # it is used to create links. Links are effectively a pointer to another file # Two types of links: hard links and soft links ln <file1> <file2> # create hard link to file1 ln -s <file1> <file2># create soft link # soft link will be removed when original file is removed. But hard link will not be removed